When it comes to drug formulations for children and adults who have difficulty swallowing pills, liquid syrups provide a convenient and effective alternative. However, for medications that require longer shelf life and stability, dry syrups are the preferred option. A growing number of dry syrup manufacturers are investing in technologies and processes to produce high-quality dry syrups, which only need to be reconstituted with water before administration.
India has emerged as a global hub for the pharmaceutical industry, with many companies excelling in both liquid and dry syrup manufacturing. This blog delves into the science, processes, and importance of dry syrup manufacturing plants, focusing on how these products are crafted, the technologies involved, and India’s leadership in this area.
What is Dry Syrup?
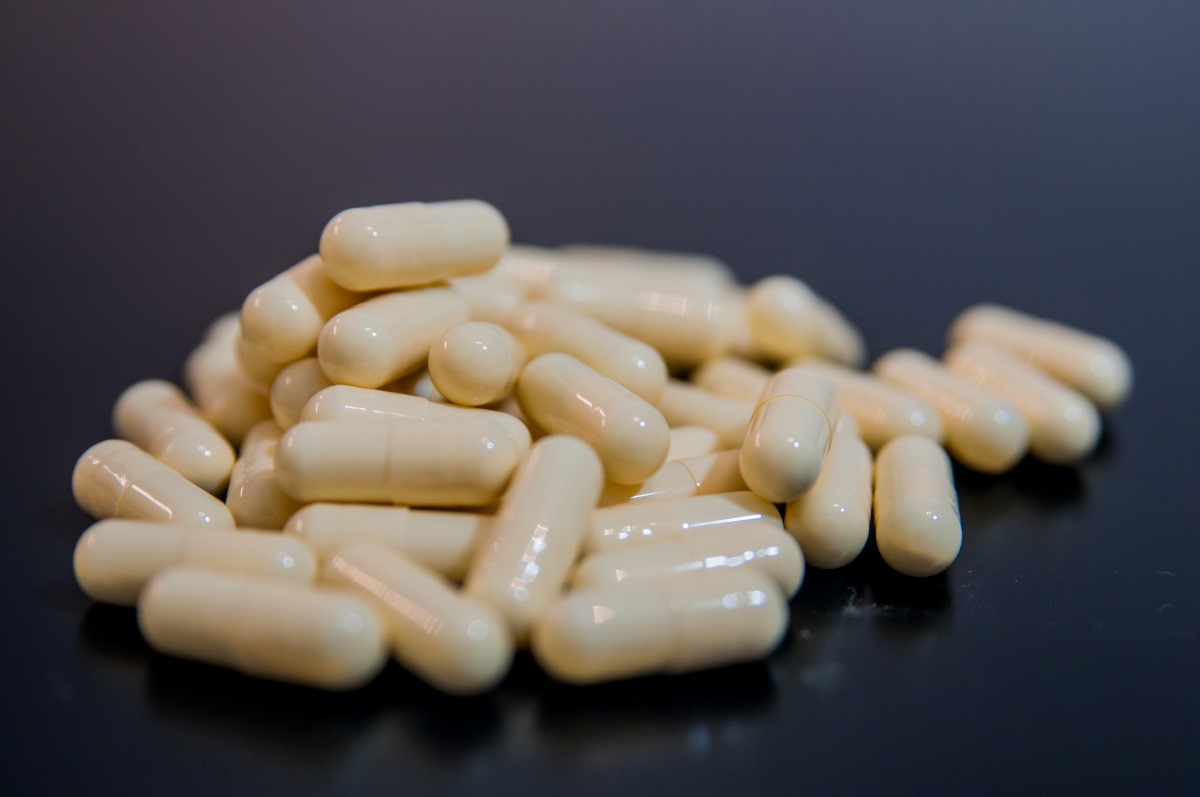
Dry syrup, also known as a reconstitutable oral suspension, is a formulation in which the active ingredient is present in powdered form and mixed with water just before use. Dry syrups are particularly useful in pediatric medicine because they allow for more flexible dosing, improved stability, and a longer shelf life compared to liquid syrups.
Unlike liquid formulations, dry syrups contain minimal water, which makes them more resistant to microbial growth. The formulation includes a combination of:
- Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Suspending agents to maintain uniformity once mixed with water.
- Flavors and sweeteners to make the medicine more palatable, especially for children.
The Science Behind Dry Syrup Manufacturing
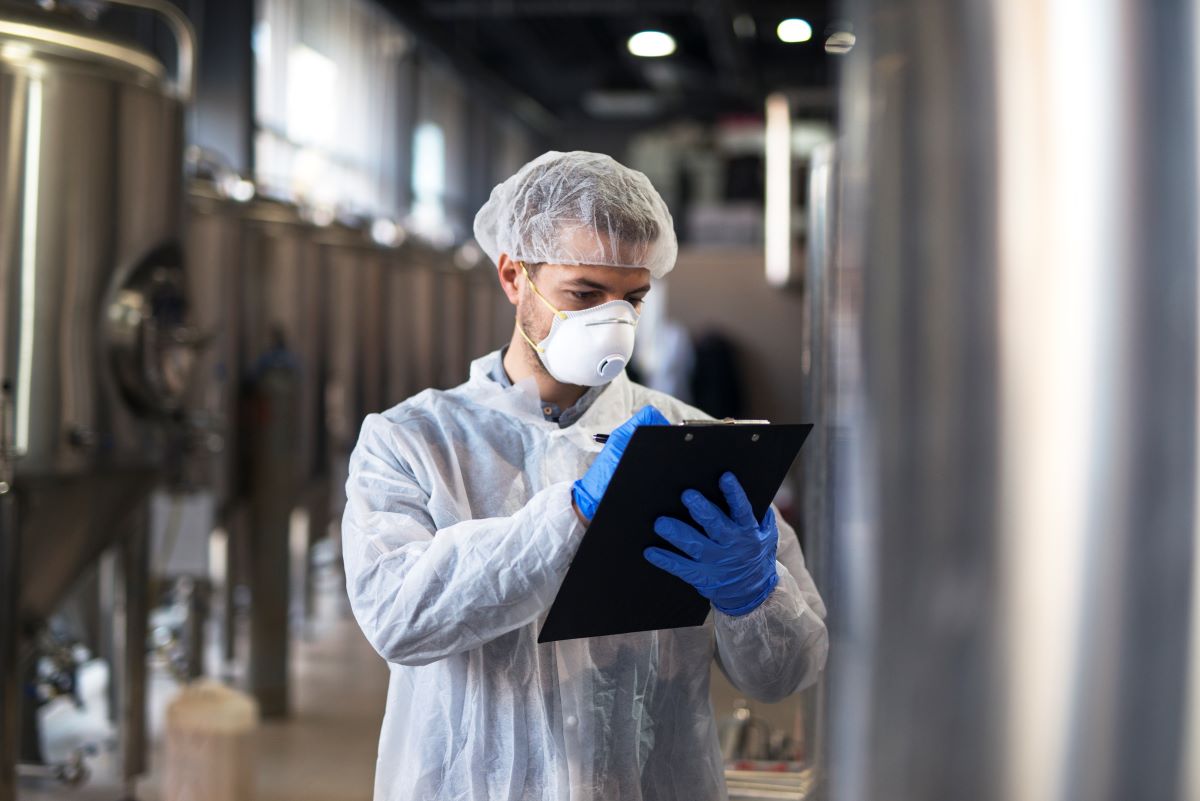
The manufacturing of dry syrup involves complex processes and strict quality controls to ensure the product is safe, stable, and effective. The key steps in the dry syrup manufacturing process include:
1. Formulation Development
The foundation of any successful syrup manufacturing plant is the formulation stage. Here, pharmacists and researchers determine the optimal concentration of the API and other excipients, including stabilizers, preservatives, and sweeteners. The challenge lies in creating a formulation that remains stable in its dry form, but also dissolves quickly and effectively when mixed with water.
One of the primary concerns during this phase is ensuring that the active ingredient doesn’t degrade over time. Some active ingredients, especially antibiotics, are highly sensitive to environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature. Therefore, stabilizers and antioxidants are used to protect the integrity of the API.
2. Granulation and Mixing
Once the formulation is finalized, the ingredients are processed through granulation—a technique that converts fine powders into larger, uniform granules. This process ensures that the dry powder flows smoothly and mixes easily with water during reconstitution.
There are two main types of granulation used in dry syrup manufacturing:
- Wet Granulation: Involves adding a liquid binder to the powder to form granules, followed by drying to remove the excess moisture.
- Dry Granulation: Uses pressure to compact the powder into granules without the need for a liquid binder. This method is ideal for moisture-sensitive ingredients.
The choice of granulation method depends on the properties of the active ingredient and the desired characteristics of the final product.
3. Drying and Milling
After granulation, the wet granules (if using wet granulation) are dried in large industrial ovens to remove any residual moisture. The dried granules are then passed through a milling process to achieve the desired particle size, ensuring the powder is smooth and free-flowing.
This step is crucial in dry syrup manufacturing because improper drying or milling can lead to uneven dosing or poor reconstitution properties.
4. Packaging
Once the formulation has been granulated, dried, and milled, it is packaged in sterile, airtight containers or bottles. Each bottle contains the correct dosage of the dry powder, and instructions for reconstitution are provided on the label. Proper packaging is essential to prevent contamination, moisture absorption, or degradation of the product during storage and transportation.
In modern syrup manufacturing plants, automated machines are used to fill and seal the bottles with precision, ensuring that each package contains the exact amount of powder.
5. Quality Control
Every batch of dry syrup undergoes rigorous quality control testing to ensure it meets regulatory standards. Tests include:
- Uniformity of the powder to ensure that each dose contains the right amount of active ingredient.
- Dissolution testing to confirm the powder dissolves quickly and evenly when mixed with water.
- Stability testing to verify that the product remains stable under different environmental conditions over its shelf life.
These tests are performed in compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and are overseen by national and international regulatory bodies like the USFDA and WHO-GMP.
India’s Role in Syrup Manufacturing
India has become a leading player in the global pharmaceutical industry, and dry syrup manufacturing is one of the key areas where the country excels. According to a report by the Indian Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF), India is responsible for producing 60% of the global vaccine supply and 20% of generic medicines worldwide, including dry syrup formulations (IBEF, 2022).
Baddi: The Pharmaceutical Hub of India
A significant portion of India’s pharmaceutical production, including dry syrup manufacturing, happens in Baddi, Himachal Pradesh. Known as the pharmaceutical hub of India, Baddi houses over 300 pharmaceutical companies (IBEF, 2021), making it a central player in both domestic and international pharmaceutical supply chains.
Many syrup manufacturers in Baddi benefit from advanced manufacturing facilities, favorable government policies, and access to a skilled workforce. The region’s strategic location also makes it an ideal hub for exporting pharmaceutical products to global markets.
The Future of Dry Syrup Manufacturing
As the demand for pediatric medicines and antibiotic treatments continues to rise, the future of dry syrup manufacturing looks promising. Industry analysts predict that the global dry syrup market will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% between 2021 and 2028, driven by the increasing prevalence of respiratory infections and other treatable conditions in children (Grand View Research, 2021).
Several trends are expected to shape the future of dry syrup manufacturing:
- Automation and AI Integration: Modern manufacturing plants are increasingly relying on automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to improve production efficiency, reduce human error, and ensure precision in formulation and packaging.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Environmental sustainability is becoming a priority for syrup manufacturing plants. Efforts to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and adopt eco-friendly packaging materials are gaining traction across the industry.
- Personalized Medicine: As personalized medicine gains popularity, dry syrup manufacturers are exploring ways to customize doses based on individual patient needs, particularly in pediatric care. This trend will likely lead to more tailored and patient-specific formulations in the future.
India has established itself as a global leader in the pharmaceutical industry, and its role in dry syrup manufacturing is critical to the world’s healthcare landscape. With cutting-edge manufacturing plants in Baddi and across the country, Indian companies are driving innovation, improving production processes, and meeting the growing global demand for high-quality dry syrups.
From formulation development to final packaging, syrup manufacturers in India are setting the benchmark for quality and efficiency in this essential area of drug delivery. As technological advancements and market demands continue to evolve, India’s dry syrup manufacturers are poised to lead the industry into a future of greater innovation, sustainability, and patient-centric care.
References:
- IBEF (2021). “Indian Pharmaceutical Industry Overview.” Indian Brand Equity Foundation.
- Grand View Research (2021). “Global Dry Syrup Market Size & Trends Analysis.”
- Niazi, S. (2019). Handbook of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Formulations. CRC Press.